This blog post is part of “The Ultimate Guide to Lead Generation” and “The Ultimate Guide to SEO” blog series. You can also check our premium B2B SEO services to boost your traffic, leads, and sales.
User experience, or UX, has become the watchword for SEO in recent years. Search engines, especially Google, work very hard to get people exactly what they are looking for as quickly as possible because happy users will come back, search more, and see more ads. Marketers are aligning their content accordingly, trying to create helpful pages that thoroughly answer questions and solve problems.
Site Performance and Other Ranking Criteria
User experience starts with site performance. Users want to find what they are searching for fast. One of the largest factors in Google’s user experience ranking is page speed. People don’t like to wait for pages to load. Backlinko’s study of one million websites’ ranking data confirms a strong connection between pagespeed and SERPs.
Fortunately, Google has a tool use can use to measure page speed and get tips on how and where you can improve it.
 Mobile experience is another important metric in search ranking. More people now search on phones and tablets than on computers, and search engines are aware that a bad mobile experience is a major turn off. The main issue of the mobile experience is that the site content needs to be “responsive,”–aware of the device being used to access the page and able deliver content in a way that is easy to consume from the device being used. This means the screen size adapts, buttons and links and large and easy to use, and more.
Mobile experience is another important metric in search ranking. More people now search on phones and tablets than on computers, and search engines are aware that a bad mobile experience is a major turn off. The main issue of the mobile experience is that the site content needs to be “responsive,”–aware of the device being used to access the page and able deliver content in a way that is easy to consume from the device being used. This means the screen size adapts, buttons and links and large and easy to use, and more.
 Mobile-friendliness is so important that Google will penalize your search rankings on all devices if it deems your mobile experience is a poor one. Fortunately, it has another test you can run on your site to measure the quality of the mobile experience and get tips on how to improve it.
Mobile-friendliness is so important that Google will penalize your search rankings on all devices if it deems your mobile experience is a poor one. Fortunately, it has another test you can run on your site to measure the quality of the mobile experience and get tips on how to improve it.
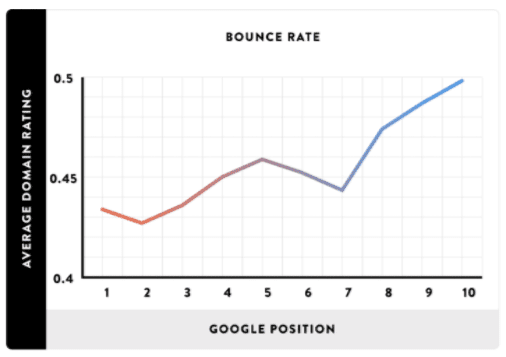
Another way Google measures UX is with bounce rates. Bounces happen when a visitor to a site leaves after viewing only one page. Google figures that if people leave after viewing one page, they didn’t find what they were looking and therefore deem it a subpar user experience. Backlinko found a strong correlation between low bounce rates and high SERPs.
Long Form vs. Short Form Content
There are many marketers that argue for short, punchy content that quickly answers questions or summarizes a personal or business issue. Others believe that in-depth, longer content is likely to be viewed as more authoritative by users and by search engines. The latter appear to be correct. Backlinko found a strong correlation between the length of the content in word count and SERPs.
They found that, “the average word count of a Google first page result is 1,890 words.”
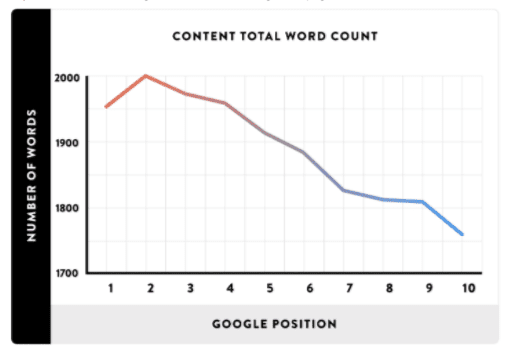
Why does longer content tend to rank higher? One theory is that longer content boosts your page’s topical relevancy, which gives search engines a deeper understanding of your page’s topic.
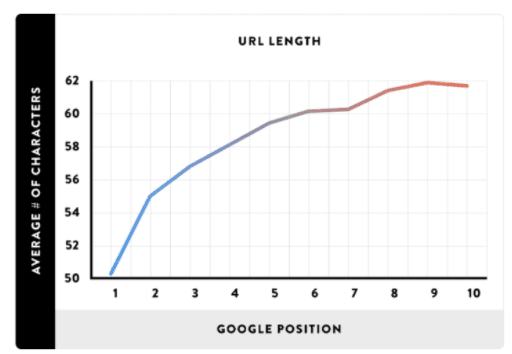
URL Length
Another unexpected finding from Backlinko’s research is that URL length appears to impact SERPs. The shorter the URL, the higher the ranking.
Matt Cutts is head of Google’s webspam team, which makes him an expert on what the search engine favors and what it doesn’t. He says this about URL length, “If you have got a three, four or five words in your URL, that can be perfectly normal. As it gets a little longer, then it starts to look a little worse. Now, our algorithms typically will just weight those words less and just not give you as much credit.”
There is much more to SEO than meets the eye. Search engines are constantly evaluating the signals that indicate that users are happy with the results that they deliver. The good news for marketers as that search engines want to help us be successful. They want to help us deliver what searchers want. For a complete guide to SEO and how to help your business’ pages rank higher, download the Alaniz Guide to SEO for 2017.
This blog post is part of “The Ultimate Guide to Lead Generation” blog series.